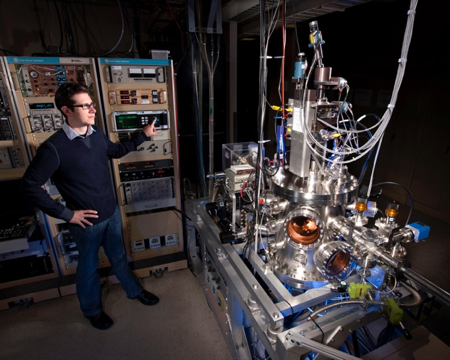
Sandia’s Hydrogen–Surface Interactions Laboratory includes an array of specialized capabilities assembled to address the obstacle of directly detecting hydrogen in furthering our understanding of hydrogen–surface interactions.
The lab includes an angle-resolved ion energy spectrometer (ARIES) for low energy ion beam analysis, developed specifically for detection of light adsorbates such as hydrogen. Sandia is also developing ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (AP-XPS) techniques and infrared spectroscopy systems (IRAS) capable of operating at near-ambient pressures.
Other advanced techniques, such as Kelvin probe force microscopy and electron energy loss spectroscopy, are also being used to study hydrogen on surfaces.