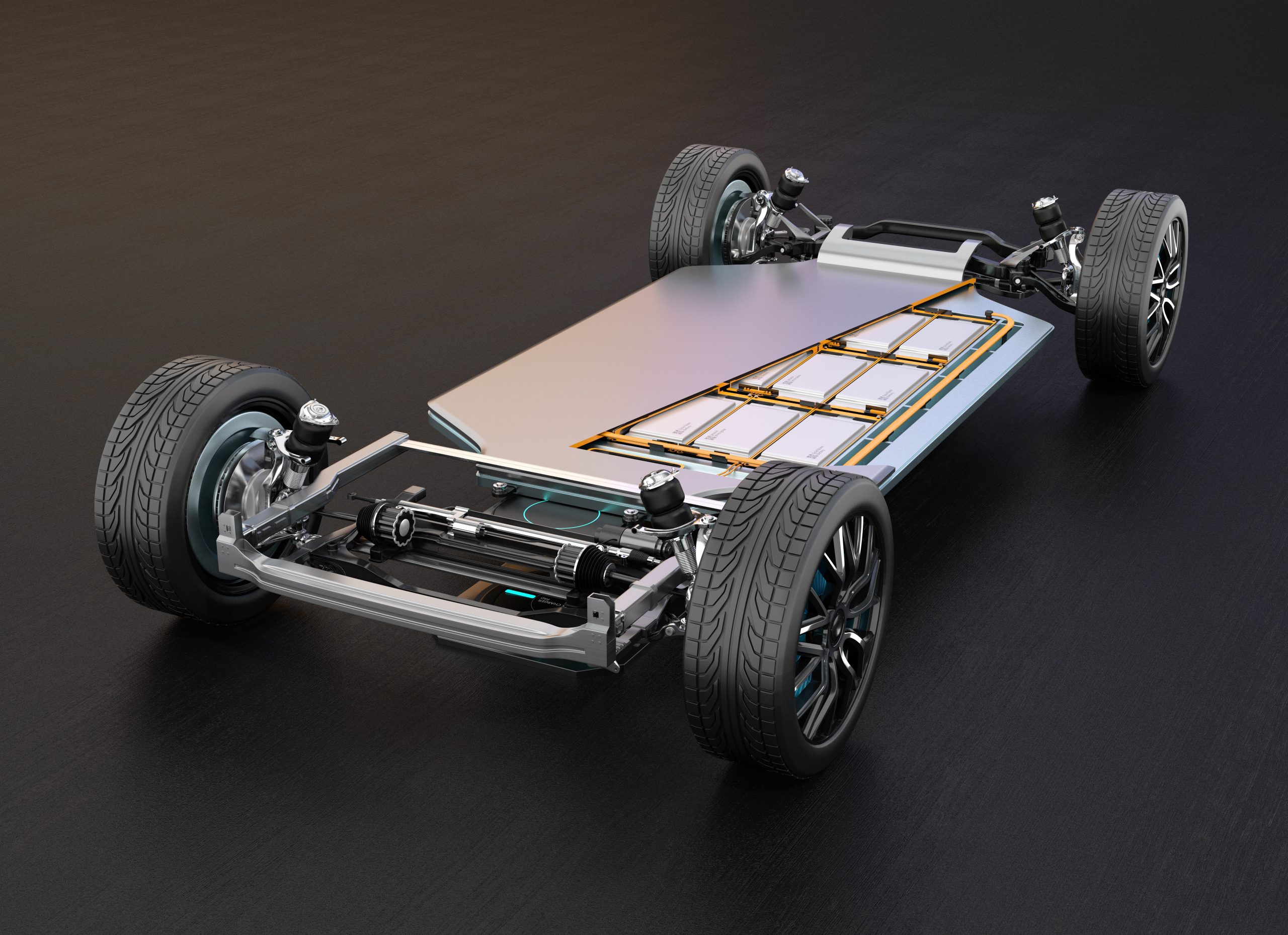

Sandia is a member of the Department of Energy’s Next-Generation Reliable Electric Drive Systems for Medium and Heavy-Duty Vehicles (NEXT-DRIVE) Consortium, a partnership with three other national laboratories (Oak Ridge National Laboratory, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, and Ames National Laboratory) as well as university collaborators. Our team is developing technologies that will improve the power density, increase the reliability, and lower the cost of next-generation drivetrains for electric vehicles. This includes research on the power electronic inverter that converts the DC voltage and current from the vehicle’s battery to AC voltage and current waveforms that power the vehicle’s motor, as well as the materials that comprise the motor itself. Sandia’s power electronics research focuses on developing and evaluating optimized materials and components including wide-bandgap (WBG) semiconductors as well as dielectric and magnetic materials (magnetic materials are also a critical component in the electric motor). Additionally, our team employs design optimization techniques that that allow us to assemble these components in the best possible circuit configuration for the inverter.
Power electronics innovation is enabled by key Sandia capabilities such as the Microsystems Engineering, Science, and Applications (MESA) microfabrication facility; the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies (CINT); the Ion Beam Laboratory (IBL); and the Distributed Energy Technologies Laboratory (DETL) microgrid test bed.
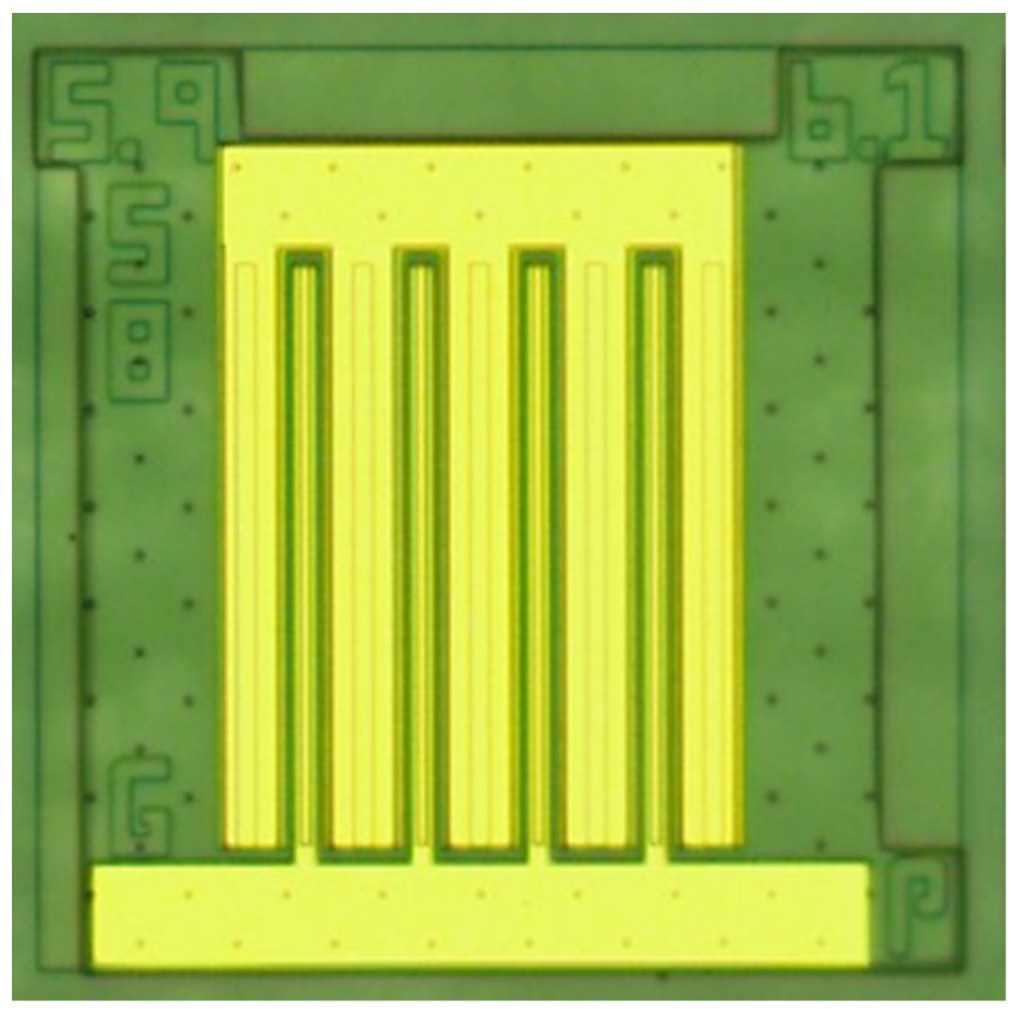

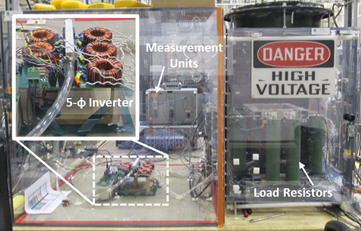
Learn more about how Sandia contributes power electronics research for electrical grid control systems.
Publications
Wide-Bandgap Power Electronics fact sheet
T. Monson et al., 2022 R&D 100 Award for Iron Nitride Soft Magnetics
Contact
Robert Kaplar
(505) 844-8285
rjkapla@sandia.gov
